Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugawara, Takanori; Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/12
Error analyses were conducted to estimate the benefit of the MA-loaded critical experiments in J-PARC on the error reduction in neutronics design of transmutation systems. By using the cross-section adjustment procedure, it was quantitatively confirmed that hypothetical MA-loaded critical experiments at TEF-P (Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility) in J-PARC would reduce the errors caused by the nuclear data for transmutation systems. For the criticality, the errors for the MA-loaded Fast Reactor (FR) and the Accelerator Driven System (ADS) were could be reduced from 0.49% and 1.03% to 0.35% and 0.80%, respectively. It was also confirmed that small experimental errors of the order of 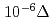 k/k are necessary for the measurement of MA fuel pin reactivity worth to improve the error caused by MA nuclear data. This experimental error level can be achieved by adopting the sample oscillation technique.
k/k are necessary for the measurement of MA fuel pin reactivity worth to improve the error caused by MA nuclear data. This experimental error level can be achieved by adopting the sample oscillation technique.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Fujita, Satoshi; Maschek, W.*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
The present study attempted the first application of SIMMER-IV to a CDA in a large-scale SFR to draw event progression and to grasp key characteristics. Since the 3-D calculation requires much computation time, the SIMMER-IV calculation focused on the early stage of the transition phase in this study. The calculation result indicated mild event progression without recriticality. Compared to a small-scale SFR, it was found that the radial sloshing reactivity was not so significant in a large-scale SFR.
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Nakajima, Ken*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2008/09
It is needless to say that the effective delayed neutron fraction, which is commonly denoted as 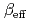 , is a very important parameter in reactor kinetics. To estimate the effective delayed neutron fraction in Monte Carlo calculations, we have applied the correlated sampling method, which is one of the Monte Carlo perturbation techniques, to the
, is a very important parameter in reactor kinetics. To estimate the effective delayed neutron fraction in Monte Carlo calculations, we have applied the correlated sampling method, which is one of the Monte Carlo perturbation techniques, to the  -ratio method. To verify the proposed methods, we have implemented them into the MVP code and performed a calculation for the effective delayed neutron fraction measured at TCA. It is found that the proposed methods give a good estimate for the effective delayed neutron fraction as well as Nauchi's and Meulekamp's methods.
-ratio method. To verify the proposed methods, we have implemented them into the MVP code and performed a calculation for the effective delayed neutron fraction measured at TCA. It is found that the proposed methods give a good estimate for the effective delayed neutron fraction as well as Nauchi's and Meulekamp's methods.
Kugo, Teruhiko; Mori, Takamasa; Yokoyama, Kenji; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Ishikawa, Makoto
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
The extended bias factor methods, the LC and the PE methods, are applied to the prediction accuracy improvement for criticality and sodium void reactivity of a traditional two-region homogeneous fast reactor core with utilizing various experimental results. The extended bias factor methods are more effective than the conventional bias factor method. The PE method is more effective than the LC method when a small number of experimental results are used because of the advantage of the former method, its higher degree of freedom in combining experimental results. The advantage hardly affects on the prediction accuracy improvement when a sufficiently large number of experimental results are used. The variances due to cross sections originally included in the design calculation values for the criticality and sodium void reactivity are almost eliminated by the extended bias factor methods with use of about 200 experimental results regarding various neutronic characteristics. The uncertainty of the criticality is considerably reduced, because the uncertainty due to cross sections largely occupies in the original total uncertainty. The uncertainty reduction in the sodium void reactivity is not so much, because the uncertainty due to cross sections is smaller than that due to calculation methods.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Nakagawa, Tsuneo; Otsuka, Naohiko*; Chiba, Satoshi; Okumura, Keisuke; Chiba, Go
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
Nuclear data for neutron induced reactions with actinides from Ac to Fm have been evaluated for JENDL Actinoid File (JENDL/AC). Almost all data in JENDL-3.3 have been updated based on available experimental data and using the newly developed theoretical model code CCONE. Integral benchmark tests for fission reactors are in progress using preliminary versions of JENDL/AC. The JENDL/AC will be released in 2008.
Takano, Kazuya; Sugino, Kazuteru; Mori, Tetsuya; Kishimoto, Yasufumi*; Usami, Shin
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
Monju core physics test analysis was performed using JAEA's neutronics calculation system with various nuclear data libraries (JENDL-3.2, JENDL-3.3, JEFF-3.1, ENDF/B-VII) for the purpose to validate the JAEA's neutronics calculation system, which utilizes JENDL-3.3. Subsequent sensitivity analysis was carried out to clarify the cause of differences in calculation results among nuclear data libraries. It is found that the calculation results obtained by JENDL-3.3 and JAEA's neutronics analysis system showed good agreement with the measured values and its accuracy is identical or better than JEFF-3.1, ENDF/B-VII in most core characteristics. Thus, the validity of JAEA's neutronics analysis system with JENDL-3.3 was confirmed. From the sensitivity analysis, it was identified that Monju can be quite valuable for the verification of the cross sections of such high-order Pu isotopes as  Pu and
Pu and  Pu and also for the validity of temperature dependency of the self-shielding using its property as a power reactor.
Pu and also for the validity of temperature dependency of the self-shielding using its property as a power reactor.
Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Umeda, Miki; Fuketa, Toyoshi; Sasajima, Hideo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Nagase, Fumihisa
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
Pulse irradiation tests of high burnup fuels were performed to assess the fuel failure limit in a postulated reactivity-initiated accident (RIA). A BWR-UO rod at a burnup of 69 GWd/t failed due to pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI). The fuel enthalpy at failure was close to those for PWR-UO
rod at a burnup of 69 GWd/t failed due to pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI). The fuel enthalpy at failure was close to those for PWR-UO rods of 71 to 77 GWd/t with more corroded cladding. Comparison of cladding metallographs between the BWR and PWR fuels showed the morphology of hydride precipitation, which depends on the cladding texture, affects the failure limit. Two tests with PWR-MOX rods of 48 and 59 GWd/t also resulted in PCMI failure. The fuel enthalpies at failure were consistent with results obtained in the previous tests with UO
rods of 71 to 77 GWd/t with more corroded cladding. Comparison of cladding metallographs between the BWR and PWR fuels showed the morphology of hydride precipitation, which depends on the cladding texture, affects the failure limit. Two tests with PWR-MOX rods of 48 and 59 GWd/t also resulted in PCMI failure. The fuel enthalpies at failure were consistent with results obtained in the previous tests with UO fuel rods, if the failure enthalpy is plotted as a function of the cladding oxide thickness. Therefore, the PCMI failure limit under RIA conditions depends on the cladding corrosion states, and the same limit is applicable to UO
fuel rods, if the failure enthalpy is plotted as a function of the cladding oxide thickness. Therefore, the PCMI failure limit under RIA conditions depends on the cladding corrosion states, and the same limit is applicable to UO and MOX fuels below 59 GWd/t.
and MOX fuels below 59 GWd/t.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Okajima, Shigeaki; Mori, Takamasa; Takeda, Toshikazu*; Kinoshita, Izumi*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2008/09
The criticality was measured in a series of mock-up cores simulated small fast reactor with massive reflector at FCA facility of JAEA in order to evaluate the prediction accuracy of the current analysis code system. In the analyses, the effective cross sections were obtained by using an ultra-fine group cell calculation code. The JENDL-3.3 cross section library was used. The core calculations for the criticality were performed by using a three-dimensional S transport code. Conventional calculations with a standard 70 energy group structure and under the P
transport code. Conventional calculations with a standard 70 energy group structure and under the P transport approximation overestimated the experimental values up to 1.5%
transport approximation overestimated the experimental values up to 1.5%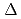
 /
/ . Furthermore, the calculation parameters were investigated concerning the fine energy group structure and the higher Legendre order of anisotropic scattering cross section. Consequently, the calculation accuracy for the criticality was improved by about 1%
. Furthermore, the calculation parameters were investigated concerning the fine energy group structure and the higher Legendre order of anisotropic scattering cross section. Consequently, the calculation accuracy for the criticality was improved by about 1%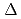
 /
/ with a 140 energy group structure and under the P
with a 140 energy group structure and under the P approximation.
approximation.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Chiba, Go; Hazama, Taira; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Ishikawa, Makoto
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
A development project of the next generation neutronics analysis code system, MARBLE, has been launched in JAEA. A software platform and common data models for fast reactor neutronics analysis were developed to realize the new system. At present, a fast reactor burnup calculation system, ORPHEUS, has been implemented in the MARBLE system. The new system reproduced benchmark results by the conventional code system and it reduced input data preparation works with the help of the capabilities supported by common data model packages. The new system was validated in an analysis of a burnup reactivity coefficient measured in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. These results show that MARBLE/ORPHEUS can be adopted as a new standard neutronics analysis system for fast reactors.
Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2008/09
To validate the reliability of nuclear data of transuranium (TRU) in the evaluated nuclear data libraries, JENDL-3.3, ENDF/B-7.0 and JEFF-3.1, a benchmark test was performed by analyzing a series of central fission rate ratios of these nuclides (CFRR) measured at the Fast Critical Assembly (FCA) of JAEA. In the test a Monte Carlo calculation code is used. C/E values are compared between these data libraries.
Thiolliere, N.*; David, J.-C.*; Eid, M.*; Konobeyev, A. Y.*; Eikenberg, J.*; Fischer, U.*; Gr schel, F.*; Guertin, A.*; Latg
schel, F.*; Guertin, A.*; Latg , C.*; Lemaire, S.*; et al.
, C.*; Lemaire, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
Gas measurements by  spectroscopy in the MEGAwatt PIlot Experiment (MEGAPIE) project has led to the determination of main radioactive isotopes released by the LBE. Comparison with calculations performed with several validated codes supplies important volatile elements release fraction estimation in a spallation target. In addition, calculations with MCNPX2.5.0, FLUKA and SNT codes coupled with evolution programs have been performed in order to study the activation of the target and structural materials. The induced database is relevant for safety and radioprotection during operation, for the post-irradiation experiments and for target dismantlement.
spectroscopy in the MEGAwatt PIlot Experiment (MEGAPIE) project has led to the determination of main radioactive isotopes released by the LBE. Comparison with calculations performed with several validated codes supplies important volatile elements release fraction estimation in a spallation target. In addition, calculations with MCNPX2.5.0, FLUKA and SNT codes coupled with evolution programs have been performed in order to study the activation of the target and structural materials. The induced database is relevant for safety and radioprotection during operation, for the post-irradiation experiments and for target dismantlement.
Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki*; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
OECD/NEA ROSA Project experiment with the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in JAEA was conducted simulating a PWR 1% cold leg small break LOCA with an assumption of high-power natural circulation due to failure of scram and total failure of high pressure injection system. The core power curve for the LSTF experiment was obtained by PWR analysis with coupled three-dimensional kinetics and thermal-hydraulics code SKETCH-INS/TRAC-PF1. A post-test analysis was performed against the obtained data by using JAEA-modified RELAP5/MOD3.2.1.2 code to validate the code predictability. The JAEA-modified RELAP5/MOD3.2.1.2 code was used by incorporating a break model that employs maximum bounding flow theory with a discharge coefficient of 0.61 for two-phase break flow. In the experiment, flow in hot legs became supercritical during two-phase natural circulation, causing the hot leg liquid level to be quite low. Liquid accumulation in steam generator U-tube upflow-side took place during reflux condensation mode. The RELAP5 code predicted reasonably well the overall thermal-hydraulic phenomena observed in the experiment, while it overpredicted the break flow rate.
Okubo, Tsutomu; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Fukaya, Yuji; Kobayashi, Noboru; Uchikawa, Sadao
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2008/09
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the well-established LWR technologies, conceptual design studies on the innovative water reactor for flexible fuel cycle (FLWR) have been performed at JAEA. FLWR is a BWR type advanced LWR concept with the triangular tight-lattice core of uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu) mixed oxide (MOX) fuel rods. Accordingly, FLWR can achieve a high conversion ratio from U to Pu in the hard neutron spectrum core. This core characteristic is also suitable for recycling of Pu and/or the minor actinides (MA) based on the fuel recycling strategy. FLWR core consists of two concepts of HC-FLWR and RMWR with different conversion ratios. It has been confirmed that even in HC-FLWR with a lower conversion ratio around 0.85 TRU recycling with about 2% MA would be possible.
DeHart, M. D.*; Gauld, I. C.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/09
Recent developments in spent fuel characterization methods have involved the development of several three-dimensional depletion algorithms based on Monte Carlo methods for the transport solution. However, most validation done to-date has been based on radiochemical assay data for spent fuel samples selected from locations in fuel assemblies that can be easily analyzed using two-dimensional depletion methods. This paper reports on the results of three-dimensional depletion calculations performed using the T6-DEPL depletion sequence of the SCALE 5.1 code system, which couples the KENO-VI Monte Carlo transport solver with the ORIGEN-S depletion and decay code, for a spent fuel sample that was extracted from the end region of the fuel rod.
Rugama, Y.*; Blomquist, R.*; Brady Raap, M.*; Briggs, B.*; Gulliford, J.*; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Suyama, Kenya; Ivanova, T.*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2008/09
Over the years, substantial progress has been made in developing nuclear data and computer codes to evaluate criticality safety for nuclear fuel handling. This state-of-the-art knowledge also has an economic impact. Increased understanding of uncertainties in safety margins allow rational and more economical designs for manipulation, storage and transportation of fissile materials. In the mid-nineties, several activities related to criticality-safety were grouped together into the Working Party on Nuclear Criticality Safety. Six expert groups co-ordinate various activities that run the gamut from experimental evaluations to code and data inter-comparisons, for the study of static and transient criticality behaviors. The various reports produced by the expert groups attempt to establish practical rules and identify applicable tools when appropriate.
Khvostov, G.*; Zimmermann, M.*; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
Komeda, Masao; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2008/09
Research reactors use a burnable poison to suppress an excess reactivity in the beginning of reactor lifetime. The JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3) has used cadmium wires of radius 0.02cm as a burnable poison. This report describes burn-up calculations of plate fuel models and full core models with MVP-BURN, which is a burn-up calculation code using Monte Carlo method and has been developed in JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency). As the results of calculations of plate models, between a model composed of one burn-up region along the radius direction and a model composed of a few burn-up regions along the radius direction, the effective absorption cross section of  Cd has had different tendency on reaching approximate 40th day (10000 MWd/t). And as results of calculations of full core model, it has been indicated that k
Cd has had different tendency on reaching approximate 40th day (10000 MWd/t). And as results of calculations of full core model, it has been indicated that k is almost same till approximate 80th day (22000 MWd/t) between a model composed of one burn-up region along the vertical direction and a model composed of a few burn-up regions along the vertical direction. However difference of
is almost same till approximate 80th day (22000 MWd/t) between a model composed of one burn-up region along the vertical direction and a model composed of a few burn-up regions along the vertical direction. However difference of  Cd burn-up becomes pronounced and each k
Cd burn-up becomes pronounced and each k makes a difference after 80th day.
makes a difference after 80th day.
Oki, Shigeo; Ogawa, Takashi; Kobayashi, Noboru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Kawashima, Katsuyuki; Maruyama, Shuhei; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Tanaka, Toshihiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2008/09
Conceptual design studies of sodium-cooled fast reactor core are performed in Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development Project (FaCT Project) in Japan. The representative MOX fuel core and the metal fuel core exert excellent performances on safety and reliability, sustainability, economic competitiveness, and nuclear non-proliferation. This paper reviews their feature in terms of reactor physics, and describes recent progress in design studies. In the recent design studies, much interest has been taken in the fuel composition change in the transition stage from light water reactors to fast breeder reactors. The core flexibility is also shown to fulfil the refined objectives such as high breeding and an enhancement of non-proliferation property.
Ishikawa, Makoto; Nagata, Takashi; Kondo, Satoru
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
In Japan, the significance of the development of fast reactor (FR) cycle technology has been seriously recognized in the national fundamental nuclear energy policy. Further, nuclear energy as a whole is indispensable worldwide to meet the expansion of energy demand and the solution of environmental problem such as global climate change. Under such circumstances, Japan launched the FR Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project in 2006. In FaCT, the design study and the R&D on innovative technologies regarding the main concept are conducted in order to present the conceptual designs of demonstration and commercial FR cycle facilities by around 2015. The main purpose of the near-term R&Ds by 2010 is to judge whether adoption of innovative technologies is feasible. The R&D program on the innovative technologies will be further extended toward 2015, with the demonstration FR expected to be operated in 2025. The concept of the FR cycle system has various aspects from the viewpoints of safety and reliability, economy, sustainability (consisting of reduction of environmental burden, waste management and efficient utilization of uranium resource), and proliferation resistance. The homogeneous recycling of an entire amount of actinides has a significant advantage from these development targets. In the present paper, we will discuss about our scenario of the homogeneous actinide recycling in the FR cycle system, based on our recent studies in the FaCT Project. The studies on the scenario of nuclear energy policy, the management and development of minor actinide (MA)-bearing fuel, reactor physics related to MA-loaded FR cores, and typical nuclear design of MA-loaded FR cores have shown the feasibility to recycle all MA in the future FR-equilibrium society. Also presented are the R&D programs to demonstrate the homogeneous actinide recycling, which are extensively conducted as one of the key national projects in Japan, as well as utilizing international cooperation.
Yagi, Takahiro*; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*; Pyeon, C. H.*; Unesaki, Hironobu*; Shiroya, Seiji*; Kawaguchi, Shinichi*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Tani, Kazuhiro*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
In order to insert a neutron detector in a narrow space such as a gap of between fuel plates and measure the fast neutrons in real time, a neutron detector with an optical fiber has been developed. This detector consists of an optical fiber whose tip is covered with mixture of neutron converter material and scintillator such as ZnS(Ag). The detector for fast neutrons uses ThO as converter material because
as converter material because  Th makes fission reaction with fast neutrons. The place where
Th makes fission reaction with fast neutrons. The place where  Th can be uses is limited by regulations because
Th can be uses is limited by regulations because  Th is nuclear fuel material. The purpose of this research is to develop a new optical fiber detector to measure fast neutrons without
Th is nuclear fuel material. The purpose of this research is to develop a new optical fiber detector to measure fast neutrons without  Th and to investigate the characteristic of the detector. These detectors were used to measure a D-T neutron generator and fast neutron flux distribution at Fast Critical Assembly. The results showed that the fast neutron flux distribution of the new optical fiber detector with ZnS(Ag) was the same as it of the activation method, and the detector are effective for measurement of fast neutrons.
Th and to investigate the characteristic of the detector. These detectors were used to measure a D-T neutron generator and fast neutron flux distribution at Fast Critical Assembly. The results showed that the fast neutron flux distribution of the new optical fiber detector with ZnS(Ag) was the same as it of the activation method, and the detector are effective for measurement of fast neutrons.